Human Rights Operations
Human rights are a fundamental component of social sustainability management, emphasizing respect for and protection of everyone's rights throughout business operations. This includes the rights of employees, customers, stakeholders, and local communities where the business operates.
Comprehensive human rights due diligence is a process used to assess and manage human rights risks that arise or may arise from business activities across the supply chain. It covers all relevant stakeholders, including at-risk and vulnerable groups. This due diligence focuses on prevention and remediation to minimize adverse impacts, in alignment with the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs), which are based on three key pillars: “Protect, Respect, and Remedy”
Human Rights Due Diligence Process (HRDD)
The company conducts a comprehensive human rights due diligence process to assess the status of operations across the entire value chain. This enables the identification, prevention, mitigation, and management of actual or potential human rights impacts arising from business operations. The process follows the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs) and the Human Rights Due Diligence Guidelines for Listed Companies issued by the Securities and Exchange Commission of Thailand (SEC). These guidelines serve as a framework for conducting comprehensive human rights due diligence, which is scheduled to be carried out every two years.
The process includes the following steps:
1. Defining the Scope of Assessment
The company has clearly defined the scope of its comprehensive human rights due diligence process to cover all relevant stakeholders, including at-risk and vulnerable groups such as children, persons with disabilities, women, minorities, migrants, third-party contract workers, indigenous peoples, local communities, LGBTQ+ individuals, the elderly, and pregnant women. This assessment applies to all operational areas where the company conducts business or has management control, as well as stakeholders within the supply chain.
The company considers key human rights issues, including labor rights, community and minority rights, supply chain rights, security and safety, environmental protection, and the rights of customers and consumers.
2. Identifying Relevant Human Rights Issues
The company reviews various human rights risk issues across the entire value chain, including both direct activities conducted by the company and indirect activities through business partners, contractors, or joint ventures that may lead to human rights violations. Additionally, the company analyzes human rights trends within the same industry at a global level and categorizes similar issues to develop and update the comprehensive Human Rights Risk Assessment checklist.
Relevant departments are assigned to identify and assess potential human rights risks arising from business operations, ensuring a thorough evaluation of human rights impacts.
The scope of the company's human rights risk and impact assessment
| Labor Rights | Local Community and Indigenous Rights | Supply Chain Rights | Security and Safety Rights | Environmental Rights | Customers and consumers Rights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Human Rights Risk Assessment
The company incorporates human rights risk issues identified in the comprehensive Human Rights Due Diligence checklist as a tool for risk assessment. A Risk Matrix is used as the assessment tool, considering the risk level of impacts and the likelihood criteria of occurrence for each human rights issue.
| Residual Risk Rating | Existing Control Assessment | Control, Monitoring, and Mitigation Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Extremely High |
|
|
| High |
|
|
| Medium |
|
|
| Low |
|
|
Risk level
The assessment of risk levels and human rights impacts is divided into four levels: low risk, medium risk, high risk, and very high risk.
Likelihood
The likelihood assessment is a criterion used alongside risk level to assist evaluators in decision-making. The likelihood assessment criteria are divided into the following levels: low, medium, high, and very high likelihood.
The relevant departments have been assigned to conduct a comprehensive human rights due diligence risk assessment, covering the business operations of the group of companies, accounting for 100% of the operational areas.
The results of the comprehensive human rights due diligence assessment in the company's business operations identified one risk issue as follows:
Environmental rights risk
A risk was identified in the area of pollution management from operations, which may have environmental impacts on the communities surrounding the factory. The assessment results indicate a medium-level risk.
4. Establishing impact mitigation and prevention measures.
The company has established preventive and mitigation measures based on the human rights risk assessment to serve as guidelines for reducing and controlling negative impacts to a low or acceptable level.
The company has prepared preventive measures and impact mitigation measures as follows:
| Risk issue | Potential risk characteristics | Preventive and mitigation measures |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
5. Monitoring and reviewing human rights performance.
The company has established key performance indicators to monitor and review measures for mitigating and controlling negative impacts from human rights risks across all identified issues. These include metrics such as the number of complaints received and resolution status. The results are regularly reported to management for review to ensure that each human rights risk issue is effectively addressed and prevented.
Additionally, as human rights issues may evolve due to changes in business activities and stakeholder expectations, the company conducts regular reviews of its human rights practices. This includes identifying and assessing human rights risks, implementing mitigation and prevention measures, and ensuring that grievance mechanisms are available for employees and stakeholders in cases of human rights violations related to the company's business activities. These efforts aim to facilitate continuous improvement and ensure the effectiveness of the company's human rights management processes.
6. Remediation and corrective actions.
The company recognizes the importance of conducting business with respect for human rights. Therefore, it has established remediation measures and compensation mechanisms for those who may be affected by human rights impacts resulting from its operations. Additionally, the company conducts lesson-learned reviews to develop preventive measures to avoid recurrence. These actions are reviewed and approved through a structured decision-making process by management to ensure accountability, build stakeholder confidence, and uphold the company’s commitments.
Welfare Committee
Recently, a labor union has not been established. However, the Company remains open to hearing employee comments and demands. In particular, the Company has officially established an independent Welfare Committee to foster dialogue and address various matters concerning employees and the workplace environment.
In this regard, employees have the right to propose their names for membership in this Committee, which will be elected. Currently, there are a total of 174 employees from the company and all affiliated organizations included in this representation. Each position within the Welfare Committee will be held for a term of 2 years, during which the Chairman of welfare committee will organize internal meetings and relay their outcomes to the executive directors in each fiscal year quarter. Furthermore, it is important to note that these Company processes are in accordance with the legal framework outlined in the Labor Protection Act B.E. 2541. This ensures policy recommendations regarding employee compensation, welfare and guarantees practical justice and equality for all employees
Social performance in 2024
GRI 2-7 (2021): Employees
GRI 405-1 (2016): Diversity of governance bodies and employees
Total Workforce
All management positions
Top Management positions
Junior Management positions
Management positions in revenue-generating functions
STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) - related positions
Nationality diversity
Share in total workforce
Share in all management positions

Employee Development Programs
Training Program “Digital Era Management Skills”
This is a training course that emphasizes general knowledge skills related to the digital society, important skills for the future world and data preparation for presentations. It covers skills for working in the digital society, analyzing, managing emotions, and understanding technology. It helps enhance organizational efficiency to keep up with the current situation and prepare for future changes. It encourages adaptation, continuous learning, and embracing new things.
Description of program objective/business benefits
To provide team leaders (L4-L5 level) with the necessary skills for operating in the digital society, such as analytical thinking, emotional management, and understanding future technologies. This training aims to prepare them for key positions within the company, ensuring their readiness for succession planning.
Quantitative Impact of Business Benefits
Employees who have undergone training have demonstrated an average increase in knowledge of 30%, as indicated by the summaries of pre- and post-training test results.
FTE participating in the program
50 persons, which represents approximately 6.35% of the total number of employees at the L4-L5 level.
Training Program “Online Content Creation”

The online content creation course covers understanding online social media platforms, particularly Facebook, Line, YouTube, Twitter, and websites. It also includes utilizing thought leaders for content dissemination in the online world. The course covers storytelling techniques, creative strategies for visual communication, and copywriting. It explores the art of word usage, emoticon utilization, cover image design, headline and title writing, and the use of software tools for online content creation, specifically targeting individuals who are not graphic designers.
Description of program objective/business benefits
- To enable learners to draw or capture images as visual content for online materials.
- To enable learners to write content that is suitable for online media.
Quantitative Impact of Business Benefits
Employees can produce 38 pieces of learning video media for the purpose of knowledge management within the organization.
FTE participating in the program
40 persons, which represents approximately 3.91% of the total number of employees at the L4-L7 level.
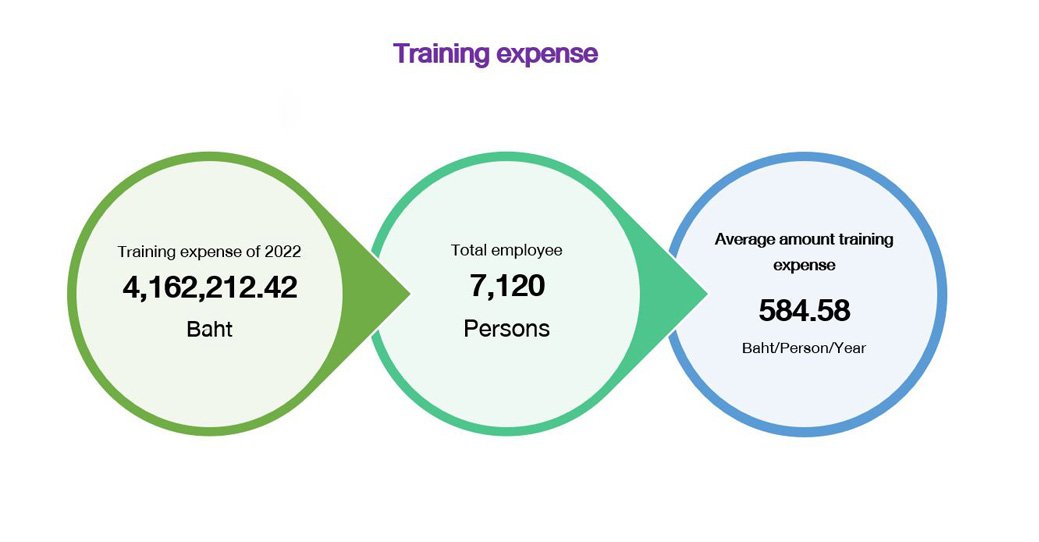
Employee Well-Being Programs
Health initiatives – BMI Challenge Program
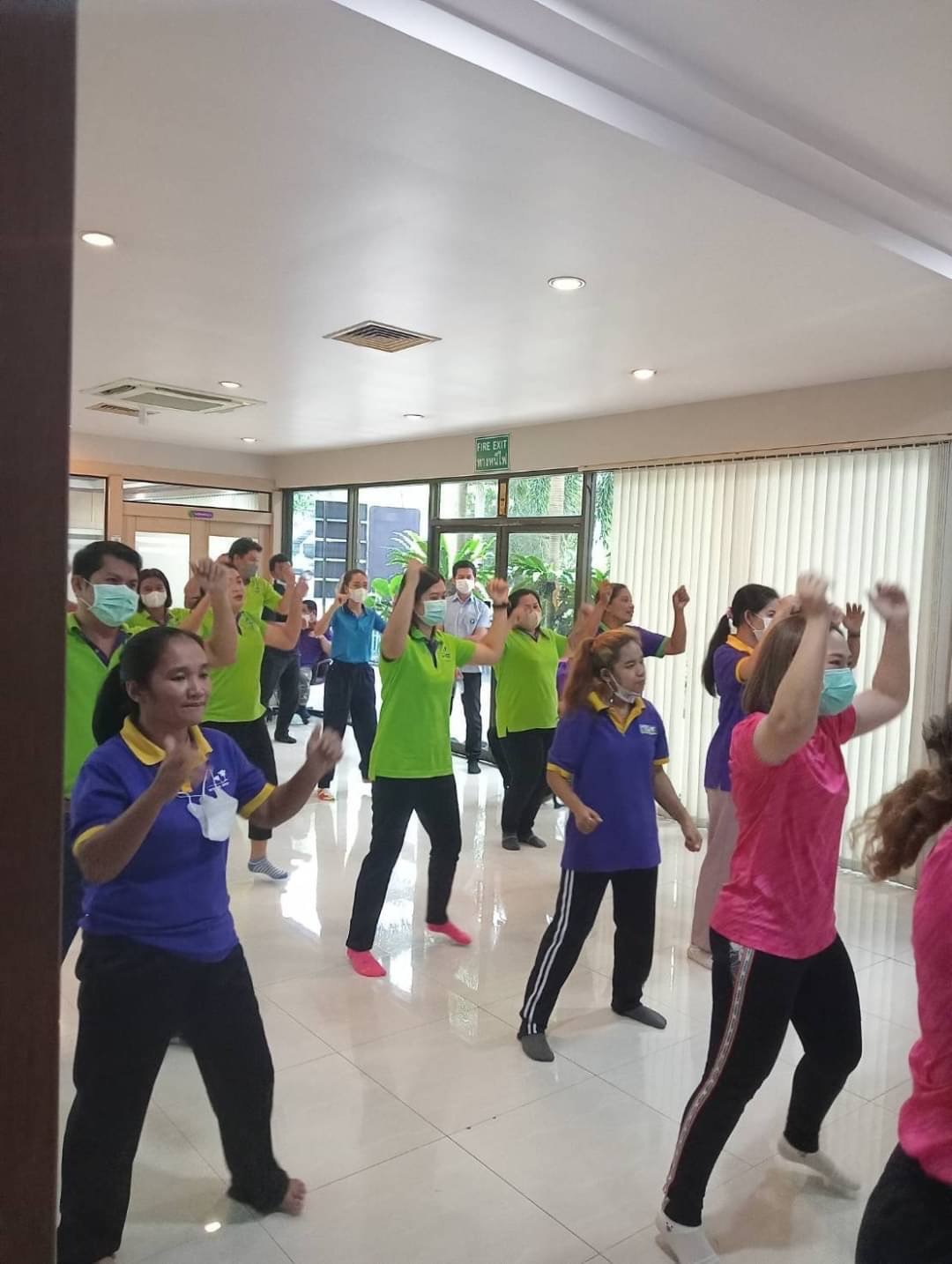
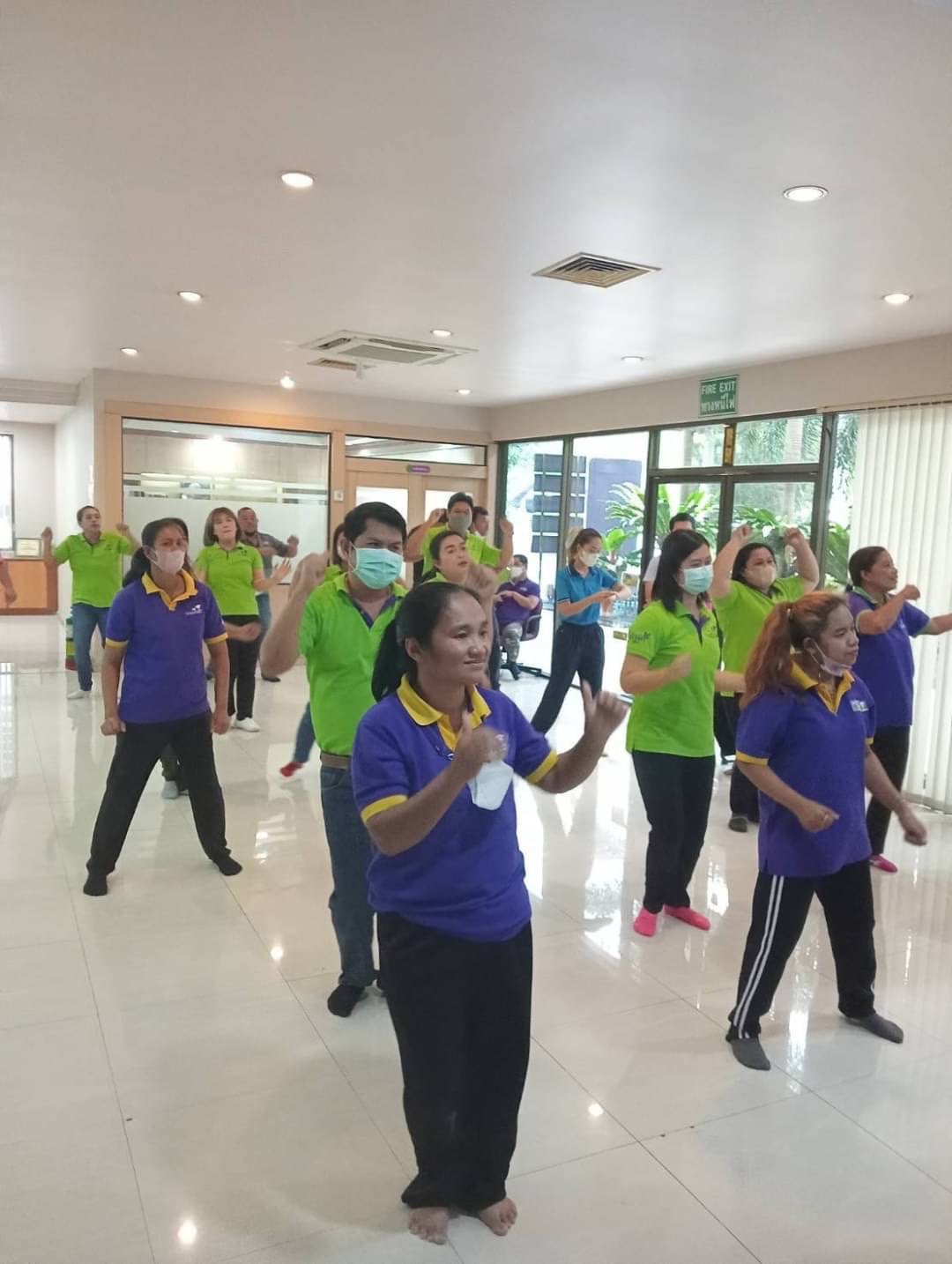


The company has “BMI Challenge Program” and expand to all branch of STA. The objective of this project is for good health and to create a habit of exercising for employees in Sri Trang Group including building good relationships and friendships with employees.
Flow of activities.
- Record BMI (Body Mass Index) of all employees before start program.
- Training / give knowledge to employees such as How to exercise correctly, good nutrition, office ergonomics etc.
- Set up morning exercise for all employees.
- The period of activity around 3-6 months.
- After finish program, record BMI of all employees and calculate the percentage of decrease BMI.
Breast -Feeding Corner Project




Equipment support
- Breast pump
- Breast pads
- Breast milk bag
- Refrigerator
- Breast milk storage bag
The Company has “Breast -Feeding Corner Project” since 2016 until now, and expand to all branch of STA. The objectives of this project are
- For employees to have a hygienic storage of breast milk.
- For allow mothers to have a convenient and clean breast pump corner.
- For morale and encouragement to employees.




